Tax Shield What Is It, Formula, How To Calculate, Examples

The relevance of depreciation tax shield in financial reporting lies in its ability to reflect the true economic cost of using an asset over its useful life, enhancing the accuracy of financial statements. By providing tax deductions, it enables businesses to invest in new assets and upgrade existing ones, ultimately driving economic growth. Overdependence on tax shields could lead to financial stress if laws change or deductible expenses decrease. Furthermore, excessive borrowing to create interest expense tax shields can lead to significant financial risk.
- Depreciation is an accounting method used to allocate costs to tangible physical assets during the course of their useful life.
- Julia Kagan is a financial/consumer journalist and former senior editor, personal finance, of Investopedia.
- This front-loads the tax shield, creating a large immediate tax benefit that can offset current income.
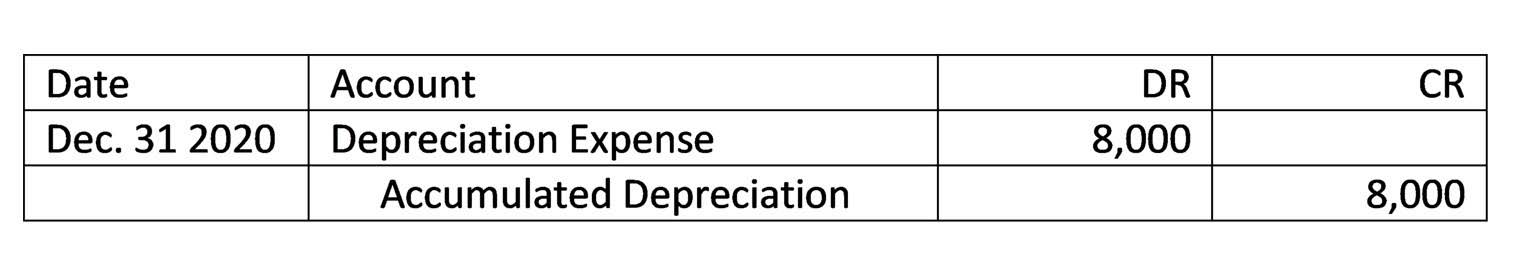
- Under U.S. GAAP, depreciation reduces the book value of a company’s property, plant, and equipment (PP&E) over its estimated useful life.
- Or, the concept may be applicable but have less impact if accelerated depreciation is not allowed; in this case, straight-line depreciation is used to calculate the amount of allowable depreciation.
Impact of Accelerated Depreciation on the Depreciation Tax Shield
- By lowering the amount subject to taxation, depreciation tax shield provides a significant advantage, bolstering the company’s financial position and ability to weather economic uncertainties.
- This deduction is the foundation of the “interest tax shield,” which makes debt financing economically cheaper than equity financing.
- When it comes to understanding the tax shield definition, understanding how to calculate it under different scenarios is important.
- The depreciation tax shield reduces taxable income, lowering overall tax liability.
- It is important to consult with an accountant or tax advisor for specific guidelines.
- Those tax savings represent the “depreciation tax shield”, which reduces the tax owed by a company for book purposes.
Both individuals and corporations are eligible to use a tax shield to reduce their taxable income. This happens through claiming deductions such as medical expenses, mortgage interest, charitable donations, depreciation, and amortization. Taxpayers can either reduce their taxable income for a specific year or choose to defer their income taxes to some point in the future. The Depreciation Tax Shield Calculator helps businesses and individuals estimate the tax savings resulting from asset depreciation. The tax shield is a valuable financial tool that reduces taxable income, allowing companies to save money on taxes while maintaining assets for long-term operations. By using this calculator, businesses can plan for tax deductions and optimize cash flow management.
Accelerated Depreciation Tax Shield
The company can also acquire the equipment on lease rental basis for $15,000 per annum, payable at the end of each year for three years. The original cost of the equipment would be depreciated at 33.3% on the straight-line method. The annual deduction is calculated using methods like the Modified Accelerated Cost Recovery System (MACRS). The core mechanism involves subtracting the allowable expense before the tax calculation occurs. This pre-tax subtraction is distinct from a tax credit, which is subtracted directly from the final tax liability. A deductible expense is not a dollar saved in taxes, but a dollar that is not taxed.
Navigating Crypto Frontiers: Understanding Market Capitalization as the North Star
This formula allows businesses to quantify tax savings due to asset depreciation, aiding in better financial planning and decision-making. The new Taxable Income is calculated as $800,000 (EBIT) minus the $100,000 Depreciation Expense, resulting in a TI of $700,000. The new tax liability is $700,000 multiplied by the https://www.bookstime.com/ 21% marginal rate, which equals $147,000. The marginal tax rate is the rate applied to the last dollar of income earned. Using this rate is necessary because the deduction reduces the highest-taxed portion of the income stream.

By minimizing taxable income, individuals and businesses can increase their after-tax cash flow, allowing for reinvestment, debt reduction, or simply saving for future goals. The tax shield is a very important aspect of corporate accounting since it is the amount a company can save on income tax payments by using various deductible expenses. The higher the savings from the tax shield, the higher the company’s cash profit. The extent of tax shield varies from nation to nation, and their benefits also vary based on the overall tax rate. If the tax rate would not change, then the marginal benefit resulting from the debt is equal to the tax balance sheet rate, and the value of company changes in proportion to the value of debt.
Want To Learn More About Finance?

By utilizing depreciation expenses as tax deductions, businesses can strategically manage their depreciation tax shield formula tax liabilities, thereby optimizing their financial resources. A Tax Shield is a reduction in taxable income that results from claiming allowable deductions like interest on debt, depreciation, amortization, or other expenses. These deductions reduce the overall tax liability, thereby “shielding” a portion of income from taxation. Although tax shield can be claimed for a charitable contribution, medical expenditure, etc., it is primarily used for interest and depreciation expenses in a company. Therefore, the tax shield can be specifically represented as tax-deductible expenses.
اترك تعليقاً